Root Paths in the Graph
There are two types of root paths, shortest and non-shortest. A shortest root path includes the minimum number of instances from a root to the selected instance. A non-shortest root path is an alternate, longer path, which also prevents the instance from being garbage collected. A non-shortest path is closely related to a hot-path reference. Each hot-path reference and non-shortest path is assigned a level, but for simplicity, level 1 paths are first explained.
Hot-path references
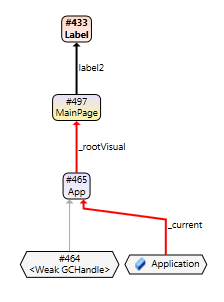
Consider the root path above. It depicts a Label instance (#433) that is prevented from being GCed by the static field Application._current. This graph indicates that it would be possible to break the root path by removing the _rootViusal reference between the App instance and the MainPage instance (by setting the MainPage._rootVisual field to null). A reference that breaks all root paths for an instance (like the _rootVisual reference) is identified as a level 1 "hot-path reference", and is colored red in the instance graph.
Non-shortest root paths
In the previous graph it also appears like it would be possible to break the root path by removing the label2 reference between the MainPage instance and the Label instance (by setting the MainPage.label2 field to null). However, this is it not the case, there are actually other, longer root paths that prevents the Label instance from being GCed. This can be seen in the graph below.
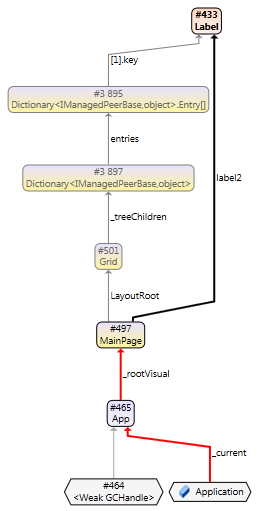
In this graph, non-shortest root paths at level 1 are also included. Clearly, there exists an additional path between the MainPage instance and the Label instance, namely a path through the Grid used as LayoutRoot. Even if the label2 reference was removed, the Label instance will still not be garbage collected, due to the additional non-shortest root path.
Higher level hot-path references and non-shortest paths
The concept of hot-path references and non-shortest paths are extended to higher levels. If it is possible to break all root paths to an instance by removing two references from the root graph, then these two references will be marked as hot-path references at level 2. If removing the two references reveals additional non-shortest root paths instead, these non-shortest root paths will be marked as level 2 non-shortest paths. This analysis then continues with higher levels, by trying to find 3 references that can be removed to break the root path, and then 4, and so on.
A hot-path reference at level 2 is colored orange in the instance graph. Higher level hot-path references are presented in an increasingly darker orange color.
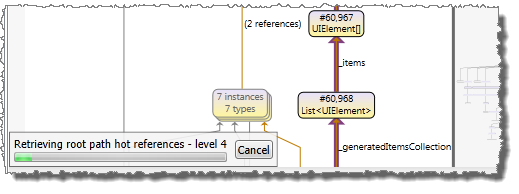
For each level the number of combinations of references will increase substantially, which can make higher level analysis take very long time. If the analysis takes too long, it can be cancelled using the Cancel button at the bottom left of instance graph.